stock options
A financial option is a financial derivative instrument that is established in a contract that gives to his buyer the right, but not the obligation,to buy (call) or sell (put) goods or values (actions, bonds, stock market indexes, etc.) at a predetermined price within a certain period.
A stock option must deal with the following points:
-Raising the stock market of the shares, increasing the stockholder´s patrimony
-Expansion in new markets, increasing of the sales
-Increase the profits, the cash-Flow, the efficiency…
-Improve the quality and services
-Reduction of the economic and financial cost
There are two types of options: call (buy´s option) and put (sell´s option)
-Call:
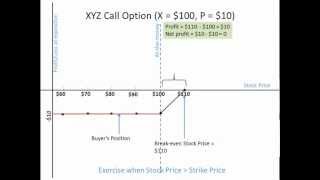
An option call gives the right to his buyer, but not the obligation, to buy a stock or other instrument at a concrete price in a specific date. The call´s option seller has the obligation to sell the asset if the buyer exercises the right to buy.
A call option is defined by the following characteristics by a financial web:
•There is an underlying stock
•There is payment due date of the call option
•There is a strike price of the option
If the stock price is going to increase, you can make profits by buying the stock or a call/put option stock.
-Put:
Put options are basically the reverse of call option: gives the owner the right, but not the obligation, to sell a stock or other instrument at a determined within a specified time.
A put option, like a call option, is defined by the following characteristics by a financial web:
•There is an underlying stock
•There is a payment due date of the put option
•There is a strike price of the put option
If the stock price is going to descend, you can make profits by shorting the stock, writing a call option on the stock or buying a put option on stock.