default
debt that the debtor has not satisfied by the end of the pre-defined term established in the debt contract. Failure to meet financial obligations.
Default is not the same as insolvency or bankruptcy, because insolvency is a legal term meaning that the debtor is unable to pay his/her debt normally due to a lack of liquidity, and bankruptcy is a legal procedure where all of the debtor’s assets are used to pay part of the debt and, subsequently, is relieved of the unpaid remaining debt. There are two possible types of default:
- Debt services default: the borrower has not covered the payment of the principal or interests.
- Technical default: a condition in the contract is violated.
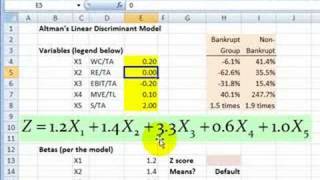
In corporate finance, the holders of the debt will usually file a petition of involuntary bankruptcy to seize any property securing the debt. There are several financial models to analyze default risk, such as the Jarrow-Turnbull model, Edward Altman’s Z-score model, or the Merton Model.